Content

Các phương pháp xử lý nước thải sản xuất giấy tái chế
Update: 05/07/2022
Share:




Wastewater Treatment in Paper Manufacturing Industry
The solution to wastewater treatment in paper manufacturing is currently the most concerning issue. How can the color in wastewater be restored up to 95% after the treatment process?
What is Paper Wastewater?
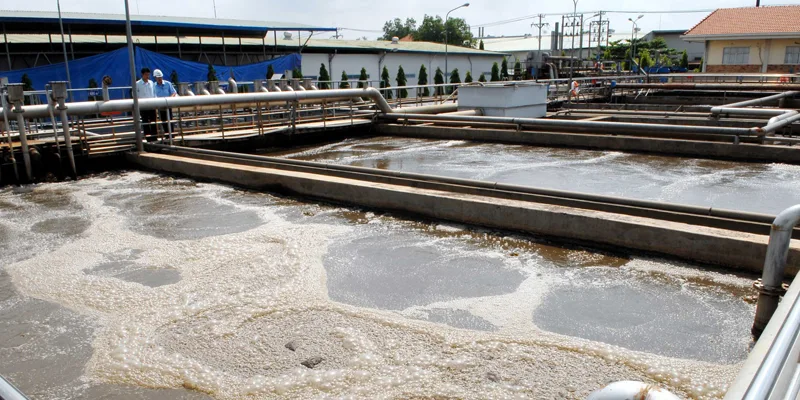
It is the wastewater generated during the paper manufacturing process. It consists of two main sources: from the paper pulping process and the working process. This wastewater is particularly difficult to treat due to its high COD content, ranging from 22,000 to 46,500 mg/l, with BOD accounting for 40-60% of COD. If it is black liquor, it is even more challenging to treat.
.webp)
Due to the high demand for diluting paper pulp to form shapes, for every 200 to 500 m3 of water used, an equivalent amount of wastewater is discharged. 20% of this will evaporate during the drying process. 60% is used for diluting paper pulp, and 20% is used in the screening and pressing stages.
In summary, for every ton of paper produced, a mill will discharge approximately 100m3 of wastewater into the environment. This is a significant amount, and most importantly, it is extremely alarming.
Why Treat Wastewater in the Paper Manufacturing Industry?
Specifically, the wastewater from this process contains a lot of Cellulose. In an oxygen-rich state, Cellulose will react to form CO2 and ethyl alcohol - two toxic substances that contribute to the greenhouse effect.
Conversely, if Cellulose is in an oxygen-deficient state, it will produce hydrogen sulfide with a very strong and unpleasant odor. In the long run, this foul odor can affect the health of workers and residents around the mill.

Therefore, to ensure environmental quality, wastewater cannot be directly discharged into ponds, lakes, rivers, or streams. Instead, an appropriate wastewater treatment process is needed to restore the quality of the water source.
Technologies and Methods for Paper Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment in the paper manufacturing industry can be based on biological and chemical principles. Currently, there are various methods for treating paper wastewater such as:
Sedimentation Method
This method separates solid particles in the form of pulp and fibers during the grinding and pulping stages. The pulp fibers and paper sludge are recovered using equipment similar to a funnel.
During the sedimentation process, operators need to calculate and monitor the appropriate time. If left for too long, the paper will decompose into foul-smelling gases.
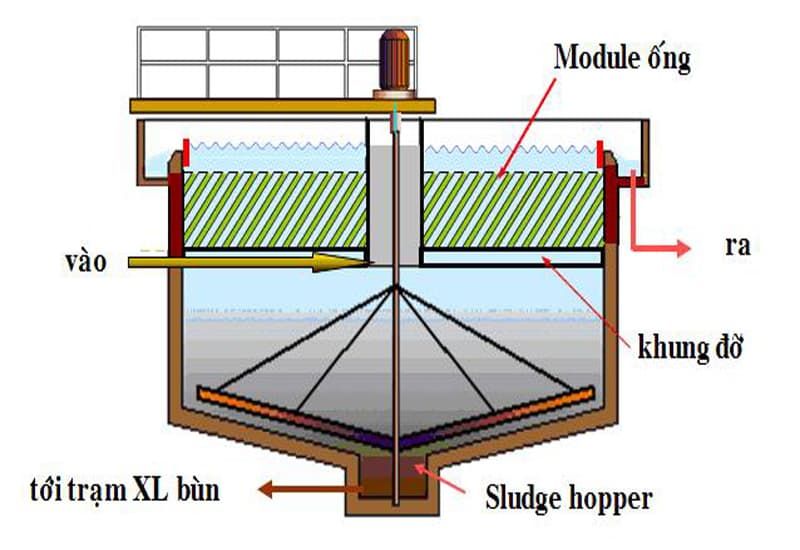
For effective sedimentation, the wastewater conditions and dirt particles must form flocs that settle easily, with a common load falling in the range of 1 - 2 m3/m2.h. This estimate will help improve efficiency and save sedimentation waiting time.
Normally, such sedimentation tanks have surface loads ranging from 5 to 10 m3/m2.h.
Coagulation-Flocculation Method
This method is used to treat suspended solid waste particles in a colloidal state, such as iron sludge, aluminum sludge, or lime compounds. It also treats phosphorus compounds, organic soluble compounds, colorless toxic substances, etc.
This wastewater treatment technology can be applied before or after the biological treatment method. Polymers are responsible for the adhesive flocculation, accelerating the sedimentation process.
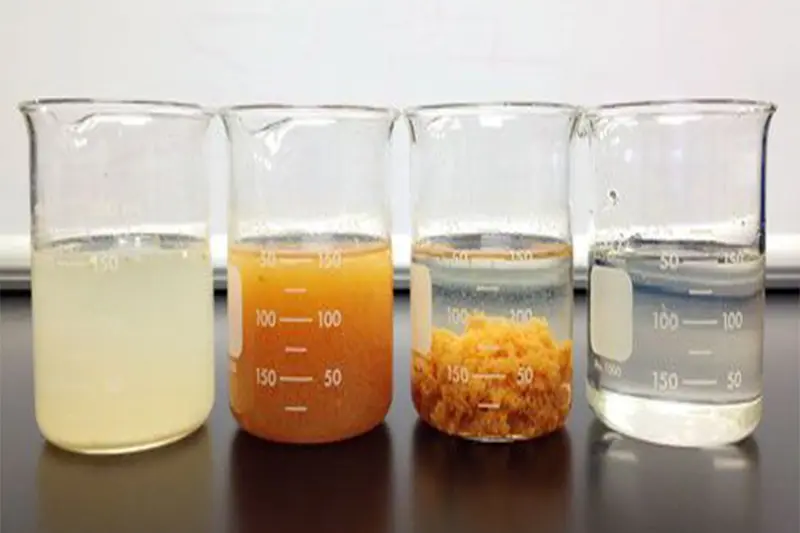

Depending on the different types of sludge, the treatment process will adjust the pH of the wastewater appropriately. For example, a pH of 5 - 7 is suitable for aluminum sludge, a pH of 5 - 11 is suitable for iron sludge, and a pH of 11 or higher is suitable for lime compounds.
Biological Treatment
This method is applied to organic compounds in soluble form. It includes paper pulp and highly organic polluted substances. Especially when the waste contains a high amount of lignin. Lignin itself does not have the ability to self-decompose into gases, but waiting for anaerobic decomposition is extremely time-consuming.
Therefore, the optimal treatment is usually done by separating the black liquor to locally treat the lignin.
Wastewater Treatment Process
- Coarse impurities are retained when reaching the trash rack.
- The wastewater continues to the sand settling tank to treat inorganic impurities.
- The wastewater is directed to the equalization tank to address flow and concentration issues.
- Proceed to the flocculation tank, where the water settles and flocculates sludge, recovering pulp. The remaining part moves to the sludge holding tank.
- Into the aerobic biological tank, the water continues to be treated for BOD and COD. This tank requires stable temperature conditions. After treatment, the water will be directed to the aerotank.
- After the aerobic tank, the water flows to the Aerotank. The remaining organic compounds in the wastewater at this stage will be almost completely treated.
- In the final stage, the tank will be disinfected with chlorine and the treated water will be returned to the natural environment.
Toan A's Paper Wastewater Treatment System
Toan A JSC provides a stable and safe wastewater treatment system throughout the operation process. The treated wastewater is guaranteed to meet the QCVN 12-MT:2015/BTNMT standard, the standard for industrial paper pulp wastewater discharged into the environment.
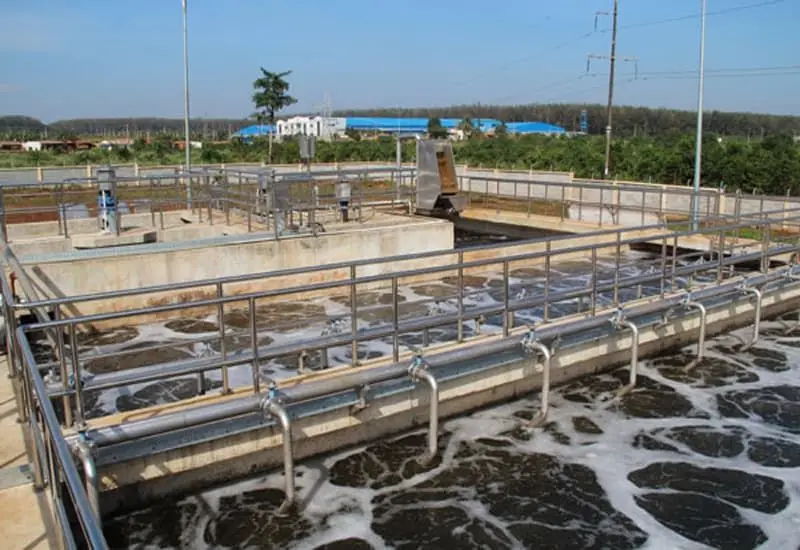

Toan A's equipment is simple, easy to operate and use, and has a long lifespan. The product not only does not consume too many user resources but also saves on treatment costs. After the wastewater filtration process, the water will be significantly reduced in organic matter content.
Toan A's paper manufacturing wastewater treatment model guarantees effective treatment for difficult-to-decompose substances. Users can also utilize biological gas sources if needed.
Some Notes on Wastewater Treatment
- Pay attention to the amount of floating foam: Many people may not notice, but floating foam is a common component in paper manufacturing wastewater.
- To treat floating foam, anti-foaming agents can be used or alkali can be added before biological treatment.
- Control color and turbidity: During production, some mills use dyes, color powders that directly affect the color and odor of wastewater.
- If the coarse debris has a size smaller than or equal to 1 µm, it will not be completely removed at the trash rack. It will only be completely blocked when it reaches the fine mesh screen.
- Compared to the primary settling tank, a DAF super deep tank can save more space and have better preliminary sedimentation efficiency. This choice is also particularly cost-effective.
- If the wastewater is directly led to the Aerotank after the anaerobic tank, the microbial content will not be thoroughly treated. Between these two tanks, you should prepare an MBBR tank, which can help treat COD up to 80%.
- To reuse the water for production, water can be taken from the rough filter tank.
With years of experience in the environmental field, Toan A JSC is always ready to answer all your questions. Contact us for advice today.
Update: 05/07/2022
Share:




Related news

Industrial wastewater refers to the contaminated water generated from industrial activities. It typically contains a variety of pollutants, such as chemicals, heavy metals, oils, and other harmful substances. The composition of industrial wastewater can v
Industrial wastewater is contaminated water that can harm human health and the environment if not properly treated. The article below will provide more information about this hazardous wastewater and how to treat it most effectively.
Created at: 05/07/2024

NIKAWA - Bringing pure water to every family
Nikawa has become a familiar name to Vietnamese consumers, offering a range of home and industrial water filtration systems. These products utilize advanced technology to completely remove impurities, bacteria, viruses, and heavy metals from water, providing users with pure and safe water.
Created at: 27/05/2024

VICAN: A reputable supplier of water filtration and wastewater treatment solutions.
Vican is a reputable brand under the Vican International Group, specializing in providing advanced water filtration and wastewater treatment solutions for various applications, ranging from households and businesses to industrial zones or large-scale projects. With over 20 years of extensive experience in the industry, Vican has established a leading position in the Vietnamese market and expanded internationally, offering optimal solutions to customers worldwide.
Created at: 27/05/2024






































































 Water Filter Columns
Water Filter Columns
 Water Filtration Membranes
Water Filtration Membranes
 Control Valves
Control Valves
 Water Filter Cartridges
Water Filter Cartridges
 Water Pumps
Water Pumps
 Water Filtration Equipment
Water Filtration Equipment
 Water Filtration Components
Water Filtration Components
 Water Filtration Materials
Water Filtration Materials
 Heat Pump Water Heaters
Heat Pump Water Heaters



 Products
Products  Solutions
Solutions  Project
Project  News
News